Mirror image enzyme constructs longest ever mirror DNA strand

Since chirally inverted DNA is more stable than its natural counterpart, it can be used to encode secret messages
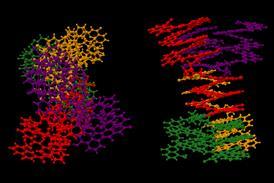
Researchers have synthesised a mirror image enzyme that allowed them to constructing the longest ever strand of mirror DNA. The team also demonstrated how this L-DNA could be used as a robust biorthogonal information repository.
Louis Pasteur first proposed the idea of a mirror image version of biological systems more than 160 years ago, following the discovery of molecular chirality. All natural DNA contains the D form of the chiral sugar deoxyribose, but it may be possible for a mirror system to be built using L -deoxyribose instead..